Climate change is a serious problem that we can no longer ignore. We are seeing rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and damage to our ecosystems, all indicating that we need to take action quickly. To reach carbon neutrality—where the greenhouse gases we produce are balanced by what we can remove or absorb—we have to rethink our economy. Every sector, including energy, transportation, and manufacturing, needs to change. This challenge requires more than just new policies; it requires real technological breakthroughs.
Technology and innovation are key to making these changes happen. New solutions in renewable energy, better infrastructure, and carbon removal are helping us cut emissions. Companies like OMARA support this effort by connecting businesses to verified climate projects. At OMARA, we also ensure transparency through a system for Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV), which builds trust in carbon markets by providing reliable data.
This article explores how technology across key sectors is helping us move toward a sustainable, carbon-neutral future.
Understanding Carbon Neutrality
Carbon neutrality means balancing the greenhouse gases we emit with the amount we remove from the atmosphere. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) states that we must achieve global net-zero emissions by mid-century to prevent serious climate impacts.
To reach this goal, we need major changes in energy, transportation, manufacturing, and agriculture. We need solutions that improve energy efficiency, support renewable energy, and capture emissions. Carbon markets also play a role by putting a value on reducing emissions, which encourages businesses to adopt cleaner technologies and innovate.
Carbon Credits: Supporting the Transition
While many industries are making progress in reducing emissions, some sectors—like heavy manufacturing, aviation, and agriculture—are still having a hard time. This is where carbon credits come in to help bridge the gap.
Carbon credits allow businesses to offset emissions they can’t avoid by purchasing verified emissions reductions or removals. Each credit represents one metric ton of carbon dioxide that has been reduced or captured through certified projects, such as renewable energy, reforestation, regenerative agriculture, carbon capture and storage, or direct air capture.
By investing in these projects, businesses can take immediate climate action while working on long-term plans to cut their own emissions. Carbon credits support global net-zero goals by making climate action possible in areas where full decarbonization takes longer.
👉 Learn how carbon credits fit into a long-term net-zero strategy.
Technology Reshaping the Energy Sector
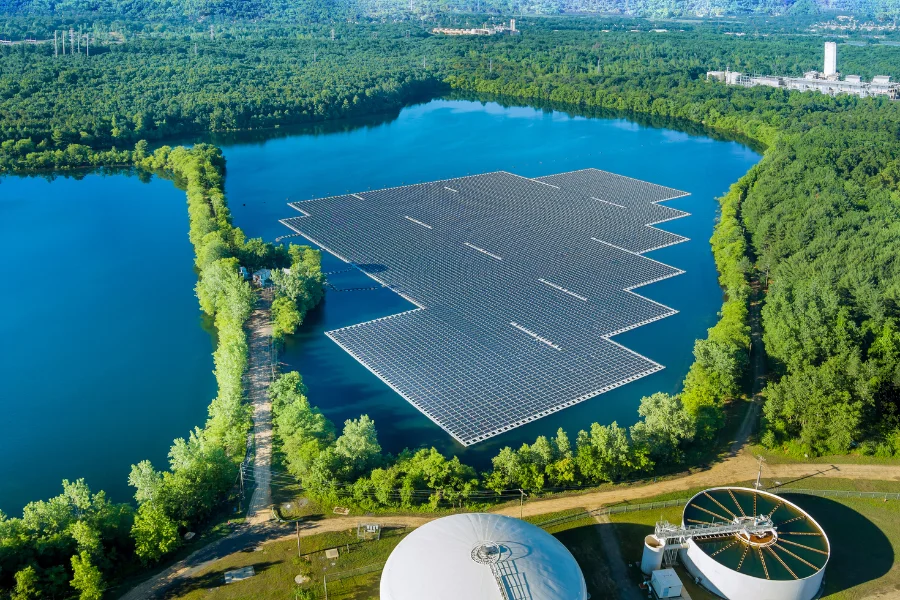

The energy sector plays a key role in achieving carbon neutrality. Innovations in solar and wind energy are making clean power cheaper and more efficient. Next-generation solar cells, such as perovskite tandem cells, can nearly double their efficiency and lower costs. Wind energy is also growing with the use of offshore and floating platforms, opening new sources of renewable energy.
Alongside generation, energy storage is advancing rapidly. Lithium-ion batteries can now store more energy for longer, while newer technologies like flow batteries and CO₂-based storage offer scaleable, cost-effective solutions for long-term energy needs.
Smart energy distribution is also crucial. Smart grids use Internet of Things (IoT) devices and artificial intelligence (AI) to predict demand and manage energy loads in real-time. Companies like Hive Power and Rebase Energy are creating systems that help integrate renewable energy into stable power networks more easily.
Transforming Transportation

The transportation sector is seeing a similar shift. Electric vehicles (EVs) now travel farther and charge faster, thanks to better batteries. This helps more people choose clean transportation. However, we still need more charging stations and better battery recycling for long-term sustainability.
For sectors where batteries are not viable, alternative fuels can help. Green hydrogen is becoming popular, especially in aviation and shipping. Innovations like HSL Technology’s HydroSil improve how we store and use hydrogen safely, while ammonia gas turbines and hydrogen fuel cells show promise for carbon-free maritime transport.
Smarter mobility solutions are also making a positive impact. Autonomous vehicles, smart traffic management, and improved urban planning help reduce traffic jams, cut waiting times, and lower emissions by promoting public transport and reducing car dependency.
Decarbonizing Industry

Heavy industries like steel and cement are also adopting new technologies to lower emissions. Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) can either reuse or permanently store captured CO₂. For example, CarbonCure injects captured carbon into concrete, making it stronger while reducing its carbon footprint.
Green hydrogen offers a clean-fuel alternative for industries that usually use fossil fuels. To increase its use, we need to make electrolyzers more efficient and improve infrastructure.
Artificial intelligence is helping optimize industrial operations. Tools like Climate TRACE use predictive analytics and digital twins to reduce waste and emissions. Additionally, using low-carbon materials and adopting circular economy practices, such as recycling and renewable resource use, help industries reduce their overall environmental impact.
Advancing Carbon Removal

Removing carbon directly from the atmosphere is crucial. Direct Air Capture (DAC) technologies pull CO₂ from the air for storage or reuse. Although DAC is currently expensive and energy-intensive, it offers strong potential for large-scale carbon removal in the future.
Nature-based solutions, such as reforestation, afforestation, and regenerative farming, also capture carbon naturally. OMARA supports these projects by offering reliable monitoring and verification, which helps ensure they are credible and have a positive impact in the carbon market.
The Role of Digital Transformation
Digital technologies are enhancing climate efforts across sectors. AI, IoT, and digital twins allow businesses to monitor their operations in real-time, optimize energy use, and reduce waste.
Blockchain technology enhances transparency in carbon markets. By creating permanent, tamper-proof records, it ensures businesses can trust that the carbon credits they purchase represent real and verified emissions reductions. This trust is essential for OMARA’s carbon credit platform.
Overcoming Challenges
Despite significant progress, we still face challenges. High costs, limited infrastructure, gaps in technology, and inconsistent policies make it harder to adopt climate solutions. To overcome these obstacles, we need ongoing innovation, targeted investments, and cooperation worldwide.
Carbon markets, like those supported by OMARA, help accelerate the adoption of new technologies and promote verified climate action globally.
OMARA’s Contribution to a Carbon-Neutral Future
At OMARA, we connect businesses with verified carbon credit projects to make climate action more accessible and more reliable. Our Digital MRV system uses data, AI analytics, and ground-level checks to ensure accurate monitoring and verification. We support a diverse range of projects, including renewable energy, nature-based solutions, and advanced carbon removal technologies. This gives businesses trusted options to meet their climate goals. Through blockchain-backed verification, we ensure that carbon credits deliver real environmental benefits.
With OMARA, businesses can offset unavoidable emissions today while contributing to scaling the technologies that will shape a net-zero future.
Toward a Carbon-Neutral Tomorrow
Technology and innovation are leading us toward a carbon-neutral future. We must continue to make progress in clean energy, transportation, industry, and digital infrastructure. OMARA helps this transition by providing clear, reliable carbon markets that allow businesses to take meaningful climate action. With ongoing innovation and global collaboration, a sustainable future is within reach.


